
Is an NFT hackable? | Unmasking the Threat
In recent years, the rise of NFTs (non-fungible tokens) has been nothing short of meteoric. With eye-popping sales of digital artwork and other collectibles, NFTs have captured the attention of ...
Education + Smart contract + Blockchain Security + How to + blog Z. Oualid today
NFTs are digital tokens that represent unique and scarce assets on the blockchain. They have become a popular way to create, buy, and sell digital art, collectibles, music, and more. But, can NFTs be malicious?
NFTs could be malicious. Even if NFTs are pieces of art, they both remain connected to a smart contract and could contain malicious code that could hurt your device.
NFTs are non-fungible tokens that can represent digital assets with unique and verifiable properties on the blockchain. They have emerged as a novel way to create and exchange value in various domains such as art, gaming, and music. However, NFTs also pose significant security and privacy challenges that must be addressed. In this blog post, I will reveal some of the dangers and pitfalls of NFTs and how you can stay safe and smart in the NFT space. Don’t miss this!
NFTs are cryptographic tokens that represent ownership or proof of authenticity of a specific digital asset. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are fungible and interchangeable, NFTs are indivisible and carry distinct properties. Each NFT is unique, and its value lies in its distinctiveness and scarcity.
NFTs are primarily created and managed on blockchain networks, with Ethereum being the most prominent platform. Blockchain technology provides transparency, immutability, and decentralization, making it an ideal foundation for NFTs. Artists and creators can mint NFTs by associating a digital asset, such as artwork, music, videos, or even virtual real estate, with a unique token. This process, known as tokenization, involves recording ownership and transaction details on the blockchain.
One of the key elements underlying NFTs is the use of smart contracts, self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions. Smart contracts enable the automation of various aspects, including royalty payments to creators and artists, allowing them to earn royalties whenever their NFTs are resold. Furthermore, NFTs can be programmed with additional functionalities, such as unlockable content or interactive features, enhancing their value and engagement.
The immutability and transparency of blockchain technology play a crucial role in establishing the authenticity and ownership of NFTs. Each NFT carries a unique identifier, which can be verified by anyone on the blockchain. This verification process ensures the integrity and provenance of the digital asset associated with the NFT, mitigating concerns of counterfeiting and fraud.
NFTs can be bought, sold, and traded on various online platforms and marketplaces, providing a thriving ecosystem for creators and collectors. These marketplaces serve as venues for artists to showcase and monetize their creations, while collectors can acquire unique digital assets and build their collections. The secondary market for NFTs enables the resale and trading of previously minted tokens, with each transaction recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparent ownership history.
To check if an image is actually an NFT or just a simple image shared on the web without any value you can do the following things:
The first step in verifying the authenticity of an NFT image involves examining its metadata. NFTs store essential information such as the creator’s name, creation date, description, and any additional attributes specific to the artwork. By scrutinizing the metadata associated with the image, one can gain insights into its origin and legitimacy. This information can typically be accessed through NFT marketplaces or blockchain explorers.
Here is a reel example of such a technique:
If you are buying an NFT from Opensea for example, you can find those metadata information in the Details section, like the following:
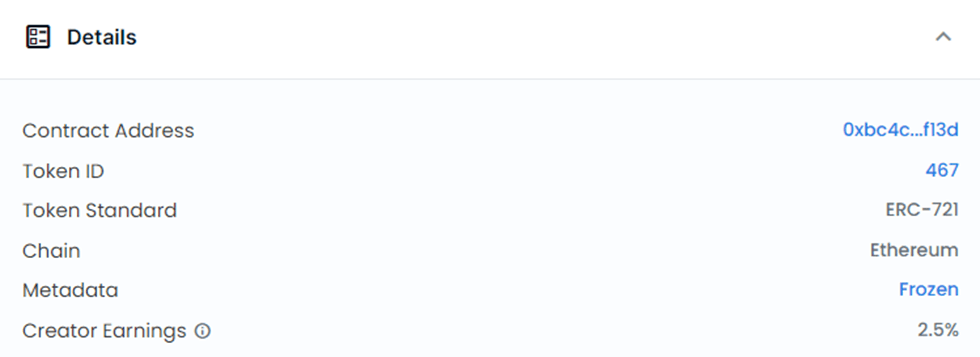
The most important elements to check the NFT in this table are:
You can use the contract address to verify if the one mentioned on the project website is the one mentioned here. Then you can call the function, tokenURI(uint256 tokenId) in that contract to check if the token exists and has a valid URI.
Once you get the URI, you can simply navigate to it as follows:

If for any reason you find that the NFT URI point to a web server then, this is just an image that could be removed at any moment, even if the ID is correct and the contract is legitimate, putting the NFT art into a centralized server make the NFT image in the risk of getting deleted at any moment.
NFTs are predominantly built on blockchain networks, leveraging their transparency and immutability. Blockchain verification is a reliable method to check the authenticity of an NFT image. By examining the transaction history associated with the NFT’s smart contract address on reputable blockchains like Ethereum, one can trace the ownership and validate the image’s authenticity. Reputable NFT marketplaces often provide links to blockchain transactions for easy verification.
Cross-referencing NFT marketplaces is another effective way to verify the authenticity of an NFT image. Reputable platforms like OpenSea, Rarible, or SuperRare curate collections of genuine NFTs. By searching for the image or associated metadata on these platforms, one can confirm if the claimed NFT is listed and authenticated by recognized marketplaces. Be cautious of listings on lesser-known or unverified marketplaces, as they may lack credibility.
Image hashing techniques offer an additional layer of verification for NFT images. Image hashing algorithms generate unique fingerprint-like hash values based on the content of an image. By comparing the hash value of the image in question with known NFT hash values, one can determine if the image is a real NFT. Popular image hashing algorithms include Perceptual Hashing (pHash), Difference Hashing (dHash), and Average Hashing (aHash).
Reverse image search engines can be a valuable tool in verifying the authenticity of an NFT image. By uploading the image to these search engines, they scan the internet for similar or identical images. If the image is associated with a known NFT or has been linked to reputable NFT marketplaces, it provides evidence of its authenticity. While not foolproof, reverse image search can provide valuable insights into the legitimacy of the image.
Some of the previously listed checking techniques could be efficient and others may not. However, combining all those techniques will certainly reduce the risk of becoming a victim of a malicious NFT.
It’s important to note that NFTs themselves do not have the inherent capability to directly hack your device. NFTs are digital assets that reside on a blockchain, and their purpose is to establish ownership and uniqueness of digital items such as artwork, music, or collectibles.
However, images can hold either malicious links in their URI or their Description. By clicking on the NFT link, you might be redirected to a dangerous website that holds malicious code. If for any reason, your browser was vulnerable and didn’t get patched before, then the malicious website might be able to hack your device. Moreover, NFTs can be distributed as files, such as videos or any kind of files. Like any other file, there is a possibility that a malicious NFT file could contain malware or be part of a larger cyber attack. Opening or downloading such files could potentially compromise the security of your device.
While NFTs themselves do not have direct capabilities to hack your wallet funds, it is important to be aware of potential security risks that can arise in the context of interacting with NFTs and related platforms. Here are a few considerations:
To protect yourself and your device when dealing with NFTs, consider the following security measures:
If you want more details about this subject I highly encourage you to take a look at the following blog post that I have written in the past few weeks:
Performing or at least asking for a smart contract auditor’s opinion about a smart contract or NFT project legitimate is a must. Some NFT projects are simply designed to steal your money once you connect your wallet with it. For more details check this blog post about honeypots in the context of smart contracts.
Written by: Z. Oualid
I am a Cyber Security Expert, I have worked with many companies around the globe to secure their applications and their networks. I am certified OSCP and OSCE which are the most recognized and hard technical certifications in the industry of cybersecurity. I am also a Certifed Ethical hacker (CEH). I hope you enjoy my articles :).

Blockchain Security Z. Oualid
In recent years, the rise of NFTs (non-fungible tokens) has been nothing short of meteoric. With eye-popping sales of digital artwork and other collectibles, NFTs have captured the attention of ...


Copyright © 2020 Getsecureworld.

Post comments (0)